Best Currencies to Invest in for Forex Traders: Unlocking Growth Opportunities
In today’s fast-paced global economy, the foreign exchange (forex) market has emerged as a prominent arena for investors seeking diverse opportunities and potential profits. With an average daily trading volume of over $6 trillion, it is the largest and most liquid market in the world. As forex traders, we understand that selecting the right currencies to invest in can be a daunting task, given the plethora of options and ever-changing market dynamics.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the best currencies to invest in for forex traders. By identifying the top-performing currencies, we hope to equip you with the knowledge required to capitalize on lucrative opportunities and make informed investment decisions. As we delve into the world of forex trading, we will explore key trends, factors to consider when selecting currencies for investment, and the top currencies to keep an eye on in 2023.
Whether you’re a seasoned forex trader or just starting, this article will serve as a valuable resource in navigating the complex landscape of currency investing. So, let’s dive in and unlock the growth opportunities that await you in the world of forex trading.
Content
I. Introduction
A. Overview of the forex market
B. Importance of currency diversification in forex trading
C. Purpose of the article – identifying the best currencies to invest in
II. Factors to Consider When Selecting Currencies for Investment
A. Economic indicators and trends
III. Top Currencies to Invest In
IV. Emerging Market Currencies
A. Overview of emerging market currencies
B. Risks and rewards of investing in emerging market currencies
V. Diversification Strategies for Forex Traders
A. Benefits of diversification in forex trading
B. How to create a diversified forex portfolio
C. Portfolio rebalancing and risk management
A. Recap of top currencies to invest in
B. Importance of staying updated on economic trends and geopolitical events
C. Emphasis on diversification and risk management in forex trading
D. Encouragement to continuously learn and adapt to the ever-changing forex market
A Overview of the Forex Market
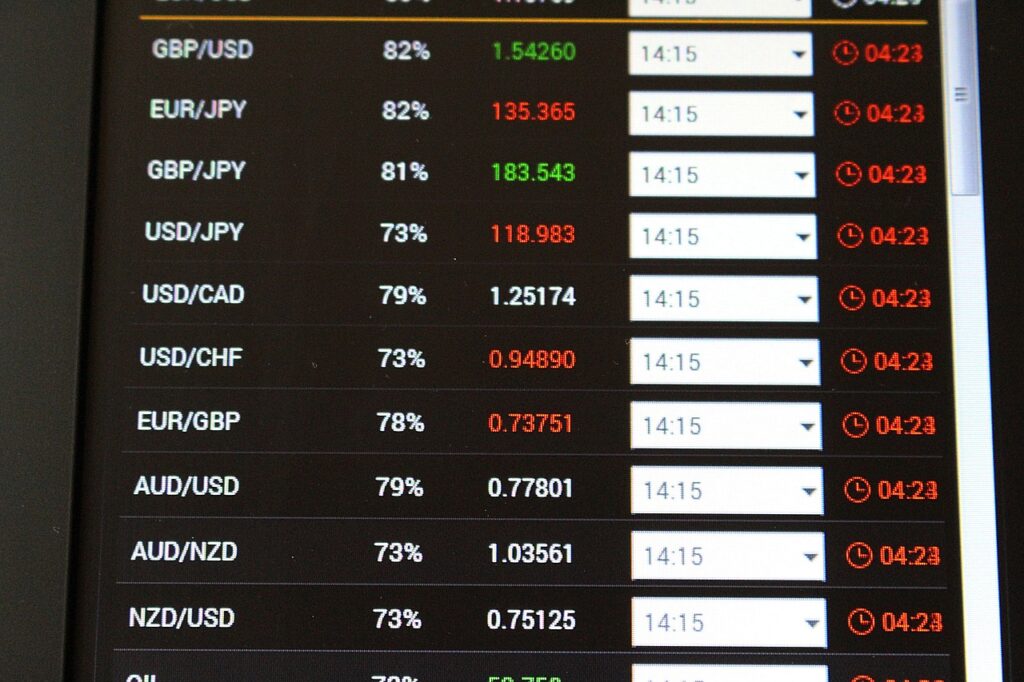
I. Introduction to the Forex Market
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a decentralized, over-the-counter (OTC) market where participants trade currencies against one another. It encompasses the conversion of one currency into another for various purposes, such as commerce, trading, or tourism. With its roots dating back to the early days of international trade and the gold standard system, the modern forex market has evolved into the largest and most liquid financial market in the world. In comparison to other financial markets like stocks, bonds, and commodities, the forex market boasts an average daily trading volume of over $6 trillion, making it an attractive arena for investors and traders seeking diversification and potential profits.
II. Key Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market comprises various participants with different motives and levels of influence. These include:
A. Central banks: As the primary monetary authorities of their respective countries, central banks play a crucial role in the forex market by implementing monetary policies, managing currency reserves, and intervening in the market to stabilize exchange rates when necessary.
B. Commercial banks and financial institutions: These entities facilitate the majority of currency transactions in the forex market, acting as market makers that provide liquidity by quoting bid and ask prices for various currency pairs.
C. Hedge funds and institutional investors: These large players actively trade in the forex market to profit from price fluctuations, hedge their investments, or diversify their portfolios.
D. Corporations: Multinational companies engage in the forex market to manage their exposure to currency risk arising from international trade, investments, and other cross-border transactions.
E. Retail traders and individual investors: With the rise of online trading platforms, retail traders can access the forex market and speculate on currency price movements, aiming to profit from short-term fluctuations or long-term trends.
III. Market Structure and Trading Sessions
The forex market operates as a decentralized, over-the-counter (OTC) market, meaning transactions are conducted electronically through a network of financial institutions rather than on a centralized exchange. Trading occurs 24 hours a day, five days a week, and is divided into four main trading sessions corresponding to the business hours of major financial centers: Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. Overlapping trading sessions, such as the London-New York overlap, often lead to increased liquidity and volatility, presenting opportunities for traders to capitalize on price movements.
IV. Currency Pairs and Quotation
In the forex market, currencies are traded in pairs, with one currency serving as the base currency and the other as the quote currency. The exchange rate represents the amount of the quote currency required to purchase one unit of the base currency. Currency pairs are broadly classified into three categories:
A. Major currency pairs: These pairs involve the US dollar (USD) and the other seven most traded currencies: Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Swiss Franc (CHF), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Australian Dollar (AUD), and New Zealand Dollar (NZD). Examples include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD.
B. Minor currency pairs: Also known as cross currency pairs, these do not involve the USD and typically include the other major currencies. Examples include EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY, and GBP/JPY.
C. Exotic currency pairs: These pairs consist of a major currency and a currency from a smaller or emerging economy, such as the Mexican Peso (MXN) or the Turkish Lira (TRY). Examples include USD/MXN and EUR/TRY.
Understanding the forex market’s structure, participants, and trading mechanics is vital for investors looking to delve into currency trading and capitalize on the numerous opportunities it presents.
B Importance of Currency Diversification in Forex Trading
Diversification is a crucial concept in the world of investing, as it helps mitigate risk and optimize returns by spreading investments across a variety of assets. In the context of forex trading, currency diversification involves trading multiple currency pairs, thereby reducing the impact of adverse movements in any single currency on the overall portfolio.
- Risk Management: By trading a diverse set of currency pairs, forex traders can lower the concentration risk associated with exposure to a single currency. For instance, if a trader’s entire portfolio consists of long positions in the EUR/USD, any unfavorable event affecting the Euro or the US dollar could lead to significant losses. Diversifying across various currency pairs helps to spread the risk and minimize the impact of such events on the trader’s portfolio.
- Exposure to Different Market Dynamics: Each currency pair has its unique characteristics and responds to different market forces. By diversifying their investments, traders can tap into various market dynamics and benefit from a range of trading opportunities. For example, while some currency pairs might be driven by geopolitical events, others may be more influenced by changes in central bank policies or economic data releases.
- Improved Performance and Stability: A well-diversified forex portfolio can lead to more consistent returns and reduced volatility. As some currency pairs may perform well during specific market conditions, a diversified portfolio can help traders take advantage of the positive performance of certain pairs while offsetting the underperformance of others.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: A diversified currency portfolio allows traders to be more flexible and adaptable in response to changing market conditions. By maintaining exposure to multiple currency pairs, traders can capitalize on new opportunities as they arise, and easily adjust their strategies to better align with the prevailing market trends.
- Access to Emerging Market Opportunities: Diversification in forex trading not only applies to major and minor currency pairs but also includes exposure to emerging market currencies. By incorporating these currencies into their portfolio, traders can benefit from the growth potential and unique dynamics of emerging markets while further spreading their risk.
In summary, currency diversification is an essential aspect of forex trading that allows traders to manage risk, take advantage of different market dynamics, and optimize returns. By trading multiple currency pairs and maintaining a well-balanced portfolio, traders can enhance their performance and stability, while staying agile and responsive to the ever-changing forex market landscape.
C. Purpose of the Article – Identifying the Best Currencies to Invest In
In the vast and dynamic world of forex trading, identifying the right currencies to invest in can be challenging, particularly for those new to the market. With numerous currency pairs and constantly evolving economic, political, and technical factors influencing their performance, selecting the most promising currencies may seem like a daunting task. The purpose of this article is to provide guidance and insights into the best currencies to invest in, based on a comprehensive analysis of various factors that impact their performance.
- Comprehensive Analysis: We will examine key factors that drive currency performance, including economic indicators, central bank policies, political stability, and technical analysis. By evaluating these factors, we aim to provide a solid foundation for selecting the most promising currencies to invest in.
- Major and Emerging Market Currencies: Our analysis will cover both major and emerging market currencies, offering a broad perspective on the opportunities available in the forex market. This approach will enable traders to diversify their portfolios effectively and tap into the unique dynamics of various currencies.
- Tailored for Forex Traders: This article is specifically designed for forex traders, addressing their unique needs and challenges when it comes to currency investing. The information provided will help traders make informed decisions, whether they are looking for short-term trading opportunities or long-term investment strategies.
- Adapting to Market Changes: The forex market is constantly evolving, with new trends and events shaping the performance of currencies. This article aims to provide traders with the knowledge and tools to continuously adapt to market changes and stay ahead of the curve.
- Empowering Traders: By identifying the best currencies to invest in, this article seeks to empower forex traders to take control of their investment decisions and achieve success in the market. Our goal is to help traders develop a clear understanding of the currency landscape and make well-informed choices that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
In conclusion, the purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide to the best currencies to invest in for forex traders, based on a thorough analysis of the factors that impact currency performance. By offering insights into both major and emerging market currencies, we aim to empower traders to make informed investment decisions and ultimately achieve success in the dynamic world of forex trading.
II. Factors to Consider When Selecting Currencies for Investment

A. Economic Indicators and Trends
When selecting currencies for investment, it is crucial to consider the underlying economic indicators and trends that influence a currency’s performance. Some key economic indicators to monitor include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP represents the total value of goods and services produced within a country over a given period. A growing GDP indicates a strong economy and may lead to an appreciation of the currency.
- Inflation: Changes in inflation rates can significantly impact a currency’s value. Central banks often target specific inflation rates, and any deviation from these targets can influence their monetary policy decisions.
- Employment Data: Employment figures, such as the unemployment rate and non-farm payrolls, provide insights into the health of an economy. High employment levels can lead to increased consumer spending and economic growth, potentially strengthening the currency.
- Interest Rates: Central banks set interest rates to manage inflation and stimulate economic growth. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the currency, while lower rates may have the opposite effect.
- Trade Balance: A country’s trade balance reflects the difference between its exports and imports. A trade surplus can lead to currency appreciation as demand for the nation’s goods and services increases, while a trade deficit may have the opposite effect.
B. Central Bank Policies
Central banks play a crucial role in the forex market as they set and implement monetary policies that directly impact currency values. Key aspects to consider when analyzing central bank policies include:
- Interest Rate Decisions: Changes in interest rates can significantly influence currency values. Traders should closely monitor central bank meetings and statements for clues on future interest rate adjustments.
- Quantitative Easing (QE) Measures: Central banks may engage in QE, a process of purchasing government bonds and other securities to increase the money supply and stimulate economic activity. This can lead to currency depreciation as the money supply expands.
- Forward Guidance: Central banks often provide forward guidance on their monetary policy intentions. This guidance can sway market expectations and affect currency values.
- Currency Interventions: In some instances, central banks may intervene directly in the forex market to stabilize or manipulate their currency’s value. Monitoring these interventions can provide valuable insights into potential currency movements.
C. Political Stability

Political stability is a critical factor to consider when selecting currencies for investment, as it can significantly impact a country’s economic prospects and currency performance. Key political factors to consider include:
- Election Outcomes: Election results can lead to policy changes that affect a country’s economic outlook and its currency’s value. Traders should monitor election cycles and potential policy shifts in countries of interest.
- Government Stability: A stable government is more likely to implement sound economic policies and maintain investor confidence. Political turmoil, on the other hand, can create uncertainty and negatively affect a currency’s value.
- Fiscal Policies: Government fiscal policies, such as taxation and public spending, can influence a country’s economic growth and currency performance. Traders should assess the impact of these policies on the currencies they intend to invest in.
D. Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can have far-reaching consequences on currency values, as they may lead to shifts in global economic dynamics, investor sentiment, and risk appetite. Key geopolitical factors to consider include:
- International Conflicts: Wars, military conflicts, and territorial disputes can create uncertainty and risk aversion in the market, potentially leading to currency depreciation in the affected countries.
- Trade Wars and Sanctions: Trade tensions and economic sanctions can disrupt global trade and impact the currencies of the involved countries. Monitoring these developments can provide insights into potential currency fluctuations.
- Major Agreements and Treaties: International agreements and treaties, such as trade deals, environmental pacts, or security alliances, can influence the economic relationships between countries and affect currency values. Keeping track of these developments can help traders gauge the potential impact on the currencies of interest.
E. Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a popular method used by forex traders to predict future price movements based on historical price patterns and market trends. Key aspects of technical analysis to consider when selecting currencies for investment include:
- Chart Patterns: Identifying and interpreting chart patterns, such as triangles, head and shoulders, or double tops and bottoms, can help traders anticipate potential price movements and make informed investment decisions.
- Trend Analysis: Analyzing market trends, including uptrends, downtrends, and sideways movements, can provide insights into the direction of currency prices and inform traders’ investment strategies.
- Technical Indicators: Various technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), or stochastic oscillators, can help traders identify entry and exit points, gauge market sentiment, and assess the strength of price movements.
By considering these factors – economic indicators and trends, central bank policies, political stability, geopolitical events, and technical analysis – traders can make more informed decisions when selecting currencies for investment. Understanding and monitoring these factors will enable traders to capitalize on potential opportunities and better navigate the complex landscape of forex trading.
III. Top Currencies to Invest In

A. US Dollar (USD)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The US Dollar (USD) is the world’s primary reserve currency and serves as a benchmark for many financial transactions. It is widely used in international trade, and global commodities are often priced in USD. As a result, the USD plays a significant role in the global economy.
- Key factors driving its strength: The USD’s strength is primarily driven by factors such as the US’s economic performance, interest rate decisions by the Federal Reserve, and global investor sentiment. During times of global uncertainty, the USD often acts as a safe-haven currency, attracting investments due to its perceived stability.
- How to trade USD in forex: USD is part of many major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD. Traders can use technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities and manage their risk exposure.
B. Euro (EUR)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The Euro (EUR) is the official currency of the Eurozone, which comprises 19 European Union countries. It is the second most traded currency in the forex market and plays a vital role in the global economy.
- Key factors driving its strength: The Euro’s value is influenced by factors such as the economic performance of Eurozone countries, monetary policy decisions by the European Central Bank, and political stability within the region.
- How to trade EUR in forex: The most traded EUR currency pair is EUR/USD. Traders can use both technical and fundamental analysis to assess potential price movements and develop trading strategies.
C. Japanese Yen (JPY)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The Japanese Yen (JPY) is the official currency of Japan and the third most traded currency in the forex market. It is often considered a safe-haven currency due to Japan’s stable economy and low-interest rates.
- Key factors driving its strength: The JPY’s strength is influenced by factors such as Japan’s economic performance, monetary policy decisions by the Bank of Japan, and global risk sentiment.
- How to trade JPY in forex: The most popular JPY currency pair is USD/JPY. Traders can use various technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
D. British Pound (GBP)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The British Pound (GBP), also known as Sterling, is the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded currency in the forex market and plays an important role in global finance.
- Key factors driving its strength: The GBP’s value is influenced by factors such as the UK’s economic performance, interest rate decisions by the Bank of England, and political developments, including Brexit-related issues.
- How to trade GBP in forex: The most popular GBP currency pair is GBP/USD. Traders can use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
E. Swiss Franc (CHF)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The Swiss Franc (CHF) is the official currency of Switzerland and is often considered a safe-haven currency due to the country’s stable economy and low-interest rates.
- Key factors driving its strength: The CHF’s strength is influenced by factors such as Switzerland’s economic performance, monetary policy decisions by the Swiss National Bank, and global risk sentiment.
- How to trade CHF in forex: The most popular CHF currency pair is USD/CHF. Traders can use various technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
F. Canadian Dollar (CAD)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The Canadian Dollar (CAD) is the official currency of Canada and is often referred to as the “loonie” due to the image of the loon on the one-dollar coin. It is a commodity-driven currency, with the Canadian economy heavily reliant on natural resources such as oil, minerals, and timber.
- Key factors driving its strength: The CAD’s strength is influenced by factors such as Canada’s economic performance, interest rate decisions by the Bank of Canada, and global commodity prices, particularly oil.
- How to trade CAD in forex: The most popular CAD currency pair is USD/CAD. Traders can use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
G. Australian Dollar (AUD)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The Australian Dollar (AUD) is the official currency of Australia and is also known as the “Aussie.” Like the CAD, the AUD is a commodity-driven currency, with the Australian economy dependent on its mining and agricultural sectors.
- Key factors driving its strength: The AUD’s strength is influenced by factors such as Australia’s economic performance, interest rate decisions by the Reserve Bank of Australia, and global commodity prices, particularly those of metals and minerals.
- How to trade AUD in forex: The most popular AUD currency pair is AUD/USD. Traders can use various technical and fundamental analysis techniques to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
H. New Zealand Dollar (NZD)
- Overview and role in the global economy: The New Zealand Dollar (NZD), also known as the “Kiwi,” is the official currency of New Zealand. The NZD is closely tied to the country’s agricultural and tourism industries.
- Key factors driving its strength: The NZD’s strength is influenced by factors such as New Zealand’s economic performance, interest rate decisions by the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, and global commodity prices, particularly those of dairy products and other agricultural goods.
- How to trade NZD in forex: The most popular NZD currency pair is NZD/USD. Traders can use a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential trading opportunities and manage risk.
IV. Emerging Market Currencies

A. Overview of emerging market currencies
Emerging market currencies refer to the currencies of countries with developing economies. These currencies often exhibit higher volatility and lower liquidity compared to their developed market counterparts. Some of the largest emerging markets include China, India, Brazil, Russia, and South Africa. While investing in emerging market currencies can offer potential for higher returns, they also come with increased risks.
B. Risks and rewards of investing in emerging market currencies
Investing in emerging market currencies can offer several rewards, including:
- Diversification: Adding emerging market currencies to a portfolio can provide diversification benefits, as they may have a low correlation with developed market currencies.
- Potential for higher returns: Emerging market economies can exhibit higher growth rates compared to developed markets, leading to the potential for higher returns on currency investments.
- Carry trade opportunities: Interest rate differentials between developed and emerging market currencies can provide carry trade opportunities, where investors borrow in low-interest-rate currencies and invest in higher-yielding currencies.
However, investing in emerging market currencies also comes with increased risks:
- Volatility: Emerging market currencies can be more volatile than their developed market counterparts, as they are often influenced by factors such as political instability, economic uncertainty, and shifting investor sentiment.
- Liquidity risk: Emerging market currencies can have lower liquidity compared to developed market currencies, making it harder to enter or exit positions at desired price levels.
- Country-specific risks: Each emerging market has unique risks related to factors such as political stability, economic policies, and geopolitical tensions.
C. Top emerging market currencies to watch
- Chinese Yuan (CNY): As the world’s second-largest economy, China plays a significant role in global trade and finance. The Chinese Yuan (CNY) has been gradually internationalized, and its influence in the forex market is expected to grow. Factors influencing the CNY include China’s economic growth, monetary policy decisions by the People’s Bank of China, and geopolitical tensions.
- Indian Rupee (INR): The Indian Rupee (INR) is the currency of the world’s fifth-largest economy, India. With a rapidly growing population and increasing economic development, the INR can offer potential opportunities for forex traders. Key factors affecting the INR include India’s economic growth, monetary policy decisions by the Reserve Bank of India, and political developments.
- Brazilian Real (BRL): The Brazilian Real (BRL) is the currency of Latin America’s largest economy, Brazil. Brazil’s economy is heavily reliant on commodities, making the BRL sensitive to fluctuations in commodity prices. Factors influencing the BRL include Brazil’s economic performance, monetary policy decisions by the Central Bank of Brazil, and political stability.
- Russian Ruble (RUB): The Russian Ruble (RUB) is the currency of Russia, a major global energy producer. The RUB is closely tied to oil prices, making it susceptible to fluctuations in global energy markets. Factors affecting the RUB include Russia’s economic performance, monetary policy decisions by the Central Bank of Russia, and geopolitical tensions.
- South African Rand (ZAR): The South African Rand (ZAR) is the currency of South Africa, a significant player in the global mining industry. The ZAR’s performance is influenced by factors such as South Africa’s economic growth, monetary policy decisions by the South African Reserve Bank, and political developments within the country.
V. Diversification Strategies for Forex Traders

A. Benefits of diversification in forex trading
Diversification is a risk management technique that involves allocating investments among various financial instruments, industries, or currencies. In the context of forex trading, diversification offers several benefits:
- Risk reduction: Diversifying across different currency pairs can help to spread risk and reduce the impact of a single currency’s poor performance on the overall portfolio.
- Enhanced returns: By investing in a variety of currency pairs with different risk profiles, traders can potentially enhance overall portfolio returns while maintaining a balanced risk exposure.
- Improved portfolio resilience: A well-diversified forex portfolio can help to minimize the impact of unexpected market events, such as political turmoil or economic crises, on overall portfolio performance.
B. How to create a diversified forex portfolio
Creating a diversified forex portfolio involves the following steps:
- Assess risk tolerance: Determine your risk tolerance level based on factors such as your investment objectives, time horizon, and financial situation.
- Choose currency pairs: Select a mix of currency pairs that align with your risk tolerance and investment objectives. This may include a combination of major, minor, and emerging market currencies.
- Allocate investments: Allocate your investments among the chosen currency pairs according to your desired risk-reward profile. This may involve overweighting lower-risk currencies or underweighting higher-risk currencies, depending on your preferences.
- Monitor performance: Regularly review the performance of your forex portfolio, taking note of any significant changes in currency values or market conditions that may warrant adjustments to your allocations.
C. Portfolio rebalancing and risk management
Portfolio rebalancing is the process of adjusting the weightings of the assets in a portfolio to maintain the desired risk-reward profile. In the context of forex trading, rebalancing involves:
- Assessing current allocations: Review your current forex portfolio allocations and compare them to your initial target allocations. If the weightings of certain currency pairs have shifted significantly due to market movements, consider rebalancing.
- Adjusting positions: To rebalance your forex portfolio, adjust your positions in the various currency pairs by either buying or selling currency to bring your allocations back in line with your target weightings.
- Implementing risk management measures: Use risk management tools such as stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and position sizing to manage risk exposure and protect your forex portfolio from significant losses.
By employing diversification strategies, creating a well-balanced forex portfolio, and regularly rebalancing and managing risk, forex traders can enhance their potential for long-term success in the currency markets.
VI. Conclusion

A. Recap of top currencies to invest in
In this article, we discussed the importance of investing in a diverse range of currencies, including major currencies such as the US Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), Japanese Yen (JPY), British Pound (GBP), Swiss Franc (CHF), Canadian Dollar (CAD), Australian Dollar (AUD), and New Zealand Dollar (NZD), as well as emerging market currencies like the Chinese Yuan (CNY), Indian Rupee (INR), Brazilian Real (BRL), Russian Ruble (RUB), and South African Rand (ZAR).
B. Importance of staying updated on economic trends and geopolitical events
Staying informed about global economic trends, central bank policies, political stability, and geopolitical events is crucial for forex traders, as these factors can significantly impact currency values and market dynamics. Keeping up-to-date with relevant news and developments will enable traders to make informed decisions and capitalize on potential opportunities.
C. Emphasis on diversification and risk management in forex trading
Diversification and risk management are critical components of a successful forex trading strategy. By creating a diversified forex portfolio and employing risk management techniques, traders can reduce their exposure to market volatility, enhance overall returns, and improve the resilience of their portfolios.
D. Encouragement to continuously learn and adapt to the ever-changing forex market
The forex market is constantly evolving, with new opportunities and challenges arising every day. To succeed in this dynamic environment, it’s essential for traders to continuously learn, adapt, and refine their trading strategies. By staying committed to ongoing education and self-improvement, forex traders can better navigate the market’s complexities and achieve long-term success.
In conclusion, investing in a diverse range of currencies, staying updated on global economic and geopolitical developments, and emphasizing diversification and risk management are all crucial components of a successful forex trading strategy. By incorporating these principles and continuously learning and adapting, traders can maximize their potential for success in the ever-changing world of forex trading.






